Ansible#
Ansible is an IT automation tool that works by connecting to nodes on a network, and then sending a small program called an Ansible module to perform some task. Ansible operates from a control node and connects to other systems using SSH and does not require a client running on the target node.
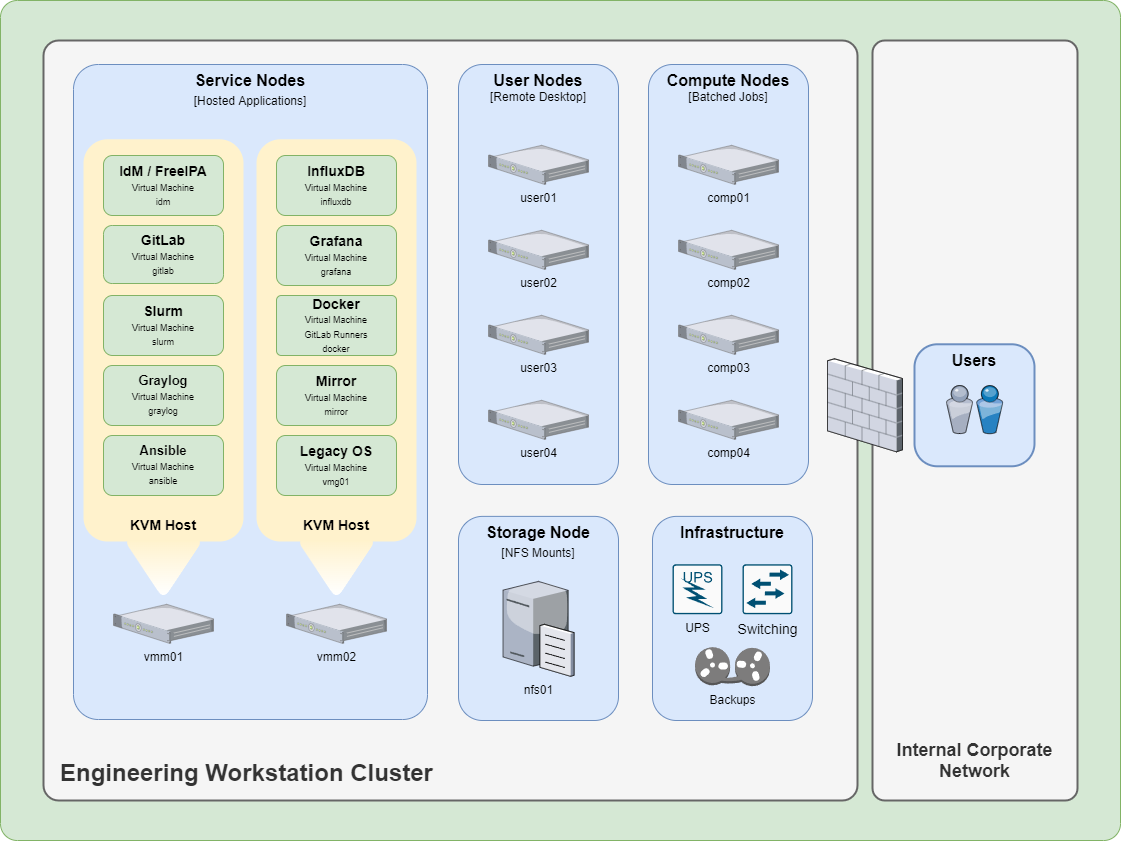
Operating Systems#
These guides are written for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 based operating systems and are compatible with AlmaLinux 8 and Rocky Linux 8.
Access Controls#
The Ansible Control node should only be accessed directly using SSH by system administrators. Standard cluster user accounts should not be able to SSH into the Ansible Control node.
An IdM manage account named “ansible” which has sudo access and used for automation tasks is recommended.
Hostnames#
These guides use the following example Hostnames and FQDN for the ansible node. FQDNs can be provided by utilizing a DNS server or installing a hosts file on the system itself.
Note
An example /etc/hosts file has been provided: hosts
Hostname |
FQDN |
Function |
Type |
IPv4 Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|
ansible |
ansible.engwsc.example.com |
Ansible Control Node |
VM Guest |
192.168.1.84 |
Guides#
The following guides are required to deploy the Ansible Control Node:
The following are Ansible usage guides: