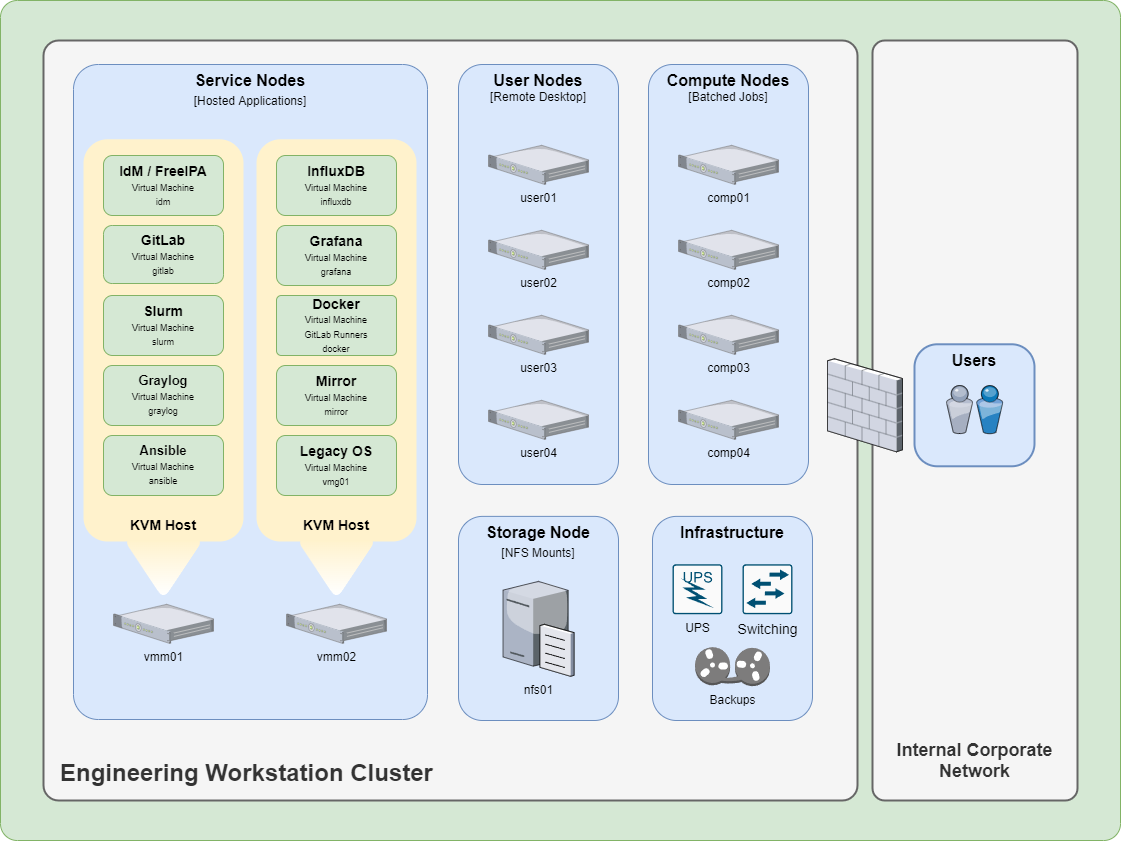
Virtual Machine Manager#
The Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) nodes are bare-metal systems that host the virtual machines that in turn host the cluster’s applications. The VMM nodes are deployed with a minimal OS installation and utilizes the Cockpit Management Console for web based management.
To ensure maximum compatibility, performance, and to improve availability the virtual machine guests should be run from local storage that utilizes redundant storage volumes. Since the physical amount and arrangement of storage can vary widely, some aspects of a system’s deployment are left up to the deploying system administrator.
Operating Systems#
These guides are written for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 based operating systems and are compatible with AlmaLinux 8 and Rocky Linux 8.
Access Controls#
The VMM nodes should only be accessed directly using SSH by system administrators. Standard cluster user accounts should not be able to SSH into the VMM nodes.
Hostnames#
These guides use the following example Hostnames and FQDN for the Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) nodes. FQDNs can be provided by utilizing a DNS server or installing a hosts file on the system itself.
Note
An example /etc/hosts file has been provided: hosts
Hostname |
FQDN |
Function |
Type |
IPv4 Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|
vmm01 |
vmm01.engwsc.example.com |
VM Manager 1 |
Bare-Metal |
192.168.1.51 |
vmm02 |
vmm02.engwsc.example.com |
VM Manager 2 |
Bare-Metal |
192.168.1.52 |
Guides#
The following guides are required to deploy the Virtual Machine Manager nodes: