Network File System#
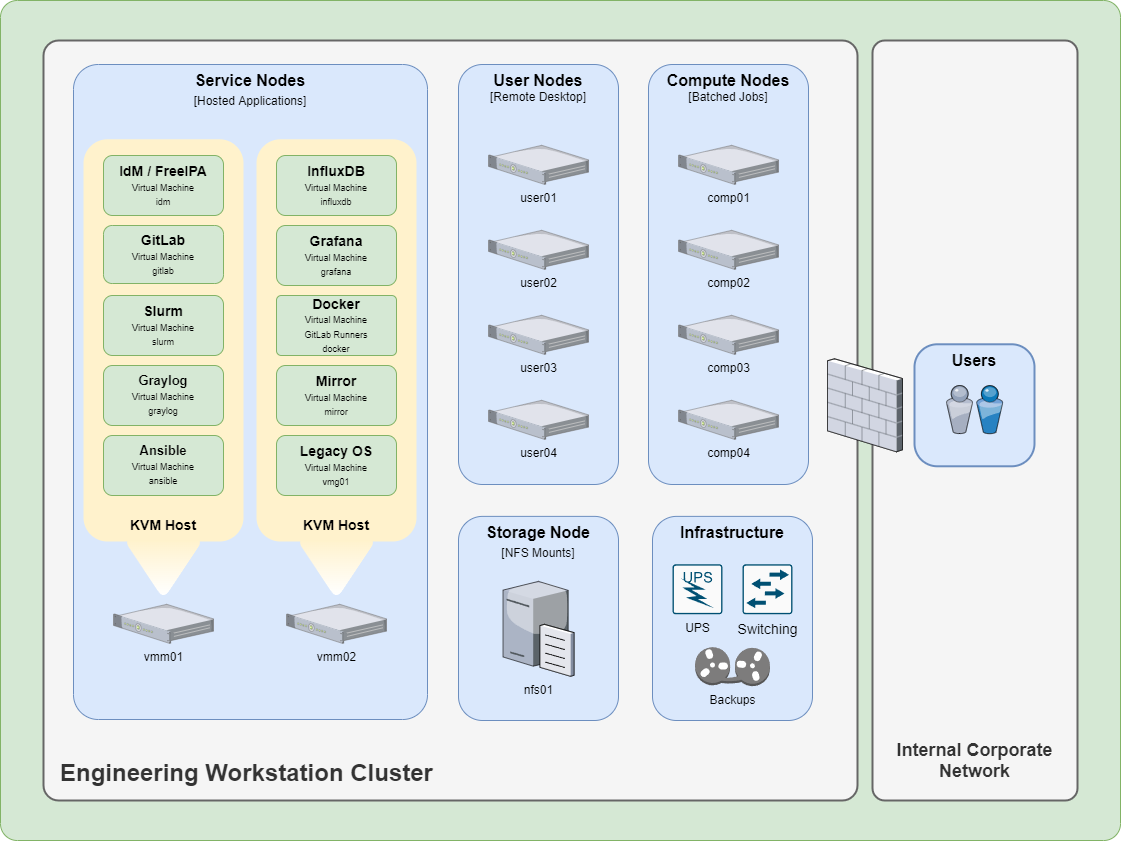
The Network File System (NFS) server node is bare-metal system that hosts the shared data resources and paths across the cluster. The NFS server node is deployed with a minimal OS installation and utilizes the Cockpit Management Console for web based management.
The NFS client is deployed on all systems that require common network shares and provides various mounts to the system depending on the role of that system.
There are many different storage solutions and configurations available in the market and some aspects of a system’s deployment are left up to the deploying system administrator. The following instructions are but one example of getting NFS hosted on the network but it is recommended that a dedicated and properly redundant storage system be used instead.
Operating Systems#
These guides are written for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 based operating systems and are compatible with AlmaLinux 8 and Rocky Linux 8.
Access Controls#
The NFS server should only be accessed directly using SSH by system administrators. Standard cluster user accounts should not be able to SSH into the NFS server node.
Hostnames#
These guides use the following example Hostnames and FQDN for the NFS Server node. FQDNs can be provided by utilizing a DNS server or installing a hosts file on the system itself.
Note
An example /etc/hosts file has been provided: hosts
Server#
The NFS server is deployed on the following node:
Hostname |
FQDN |
Function |
Type |
IPv4 Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|
nfs01 |
nfs01.engwsc.example.com |
NFS Storage |
Bare-Metal |
192.168.1.50 |
Clients#
The NFS client is deployed on the following nodes which will utilize the mounts hosted by the NFS Server:
Hostname |
FQDN |
Function |
Type |
IPv4 Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|
nfs01 |
nfs01.engwsc.example.com |
NFS Storage |
Bare-Metal |
192.168.1.50 |
user01 |
user01.engwsc.example.com |
User Node 1 |
Bare-Metal |
192.168.1.60 |
user02 |
user02.engwsc.example.com |
User Node 2 |
Bare-Metal |
192.168.1.61 |
user03 |
user03.engwsc.example.com |
User Node 3 |
Bare-Metal |
192.168.1.62 |
user04 |
user04.engwsc.example.com |
User Node 4 |
Bare-Metal |
192.168.1.63 |
comp01 |
comp01.engwsc.example.com |
Compute Node 1 |
Bare-Metal |
192.168.1.64 |
comp02 |
comp02.engwsc.example.com |
Compute Node 2 |
Bare-Metal |
192.168.1.65 |
comp03 |
comp03.engwsc.example.com |
Compute Node 3 |
Bare-Metal |
192.168.1.66 |
comp04 |
comp04.engwsc.example.com |
Compute Node 4 |
Bare-Metal |
192.168.1.67 |
idm |
idm.engwsc.example.com |
Identity Management |
VM Guest |
192.168.1.80 |
gitlab |
gitlab.engwsc.example.com |
GitLab CE |
VM Guest |
192.168.1.81 |
slurm |
slurm.engwsc.example.com |
Slurm Controller |
VM Guest |
192.168.1.82 |
graylog |
graylog.engwsc.example.com |
Graylog Open |
VM Guest |
192.168.1.83 |
ansible |
ansible.engwsc.example.com |
Ansible Control Node |
VM Guest |
192.168.1.84 |
influxdb |
influxdb.engwsc.example.com |
InfluxDB |
VM Guest |
192.168.1.85 |
grafana |
grafana.engwsc.example.com |
Grafana |
VM Guest |
192.168.1.86 |
docker |
docker.engwsc.example.com |
Docker Host |
VM Guest |
192.168.1.87 |
mirror |
mirror.engwsc.example.com |
DNF Repository Mirror |
VM Guest |
192.168.1.88 |
vmg01 |
vmg01.engwsc.example.com |
Legacy OS (Optional) |
VM Guest |
192.168.1.89 |
Guides#
The following guides are required to deploy the NFS server:
NFS Client Deployment Guide (The server can also be a client)
The following guides are required to deploy the NFS client: